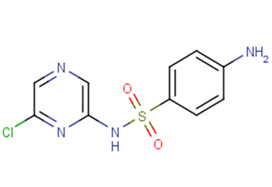
Sulfachloropyrazine sodium
CAS No. 102-65-8
Sulfachloropyrazine sodium( Sulfachloropyrazine | Sulfaclozine )
Catalog No. M20626 CAS No. 102-65-8
Sulfachloropyrazine sodium is an antiprotozoalwith antibacterial and anticoccidial effects.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSulfachloropyrazine sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSulfachloropyrazine sodium is an antiprotozoalwith antibacterial and anticoccidial effects.
-
DescriptionSulfachloropyrazine sodium is an antiprotozoalwith antibacterial and anticoccidial effects.
-
In VitroThe elimination of Sulfaclozine in the three systems: UV/TiO2, UV/K2S2O8, and UV/TiO2/K2S2O8. Sulfaclozine is weakly adsorbed on the surface of TiO2 at pH 7 (< 5%) but efficiently eliminated with the following three systems: UV/TiO2, UV/K2S2O8, and UV/TiO2/K2S2O8 in ultra pure water. Moreover, 12 of Sulfaclozine by-products are identified and reaction pathways show that, in addition of ?OH and SO4?? radicals, the conduction-band electrons are responsible for the formation of some main by-products either directly or by the formation of superoxide radicals.
-
In VivoSulfaclozine (60 mg/kg; intravenous injection or oral administration; male broiler chickens) can be used primarily for the treatment of parasitic and microbial infections of the digestive tract rather than for the treatment of systemic infections. Animal Model:14 male broiler chickens (30-day-old) Dosage:60 mg/kgAdministration:Intravenous injection or oral administration (Pharmacokinetic Analysis)Result:Serum drug concentrations at 0.083, 0.50, 2, 6, 24 and 72h were determined to be 99.62, 83.50, 72.68, 58.43, 38.66 and 13.14 μg/mL, respectively, by intravenous injection. By oral administration were determined as 4.33, 7.95, 16.46, 22.88, 16.03 and 5.74 μg/mL, respectively.
-
SynonymsSulfachloropyrazine | Sulfaclozine
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
Recptorbacterial|Parasite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number102-65-8
-
Formula Weight284.72
-
Molecular FormulaC10H9ClN4O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:29 mg/mL (101.85 mM)
-
SMILESNc1ccc(cc1)S(=O)(=O)Nc1cncc(Cl)n1
-
Chemical Name4-Amino-N-(6-chloropyrazin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sentepe I Eraslan G. Pharmacokinetic of sulfaclozine in broiler chickens[J]. Food & Chemical Toxicology An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2010 48(1):0-451.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Loganetin
Loganetin, a non-toxic natural product, shows antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections.
-
ClpB-IN-1
ClpB-IN-1 is a potential antimicrobial agent.ClpB-IN-1 is a potent ClpB inhibitor.
-
Proflavine
Proflavine (3,6-Diaminoacridine) is a disinfectant bacteriostatic against many gram-positive bacteria and is a topical antiseptic used mainly in wound dressings.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


